Truth Tables for Conditionals Worksheets
What Are the Trends of Truth Tables for Conditionals?
The basics of mathematical logic goes with the if and is conditional statements. A conditional statement, symbolized by p → q, is an if-then statement in which p is a hypothesis and q is a conclusion. The logical connector in a conditional statement is denoted by the symbol →. The conditional is defined to be true unless a true hypothesis leads to a false conclusion. The table for truth statements goes as follows:
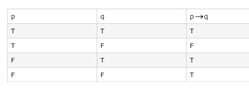 In the truth table above, p → q is only false when the hypothesis (p) is true, and the conclusion (q) is false; otherwise, it is true. It means there are more chances for a statement to be true then to be false. If a true hypothesis leads to a false conclusion, then the conditional statement is considered true.
Note: A conditional statement is a compound statement.
In the truth table above, p → q is only false when the hypothesis (p) is true, and the conclusion (q) is false; otherwise, it is true. It means there are more chances for a statement to be true then to be false. If a true hypothesis leads to a false conclusion, then the conditional statement is considered true.
Note: A conditional statement is a compound statement.
-
Intermediate Lesson
Shows students how to determine truth values for Conditionals. Use a truth table to determine the possible truth values of the given statement.
View worksheet -
Independent Practice 1
Contains a mixture of problems using Conditionals. Students must determine the truth value. Using the tables below, determine the truth values of the following statements.
View worksheet -
Independent Practice 2
Features truth value questions with assorted concepts. Students concentrate on Conditionals.
View worksheet -
Homework Worksheet
Features 6 conditional problems; students must determine the truth-value.
View worksheet -
Skill Quiz
10 truth value questions that include Conditionals. Scoring matrix is provided.
View worksheet